RedwoodJS is a full-stack JavaScript framework that integrates frontend and backend development into a single unified workflow. It’s designed for building and deploying modern web applications using React, GraphQL, and Prisma.
In this guide, we’ll walk through deploying a RedwoodJS application on an Ubuntu server using CloudRay. This article assumes you already have a RedwoodJS project hosted in a Git repository. If you’re just getting started with RedwoodJS, check out the Quick Start Guide to scaffold your first app.
Contents
- Adding Servers to CloudRay
- Create a Deployment Script
- Define the Variable Group
- Run the Deployment Script
- Next Step
- Summary
Adding Servers to CloudRay
Before getting started, make sure your machine is added to a CloudRay project and connected using the CloudRay Agent.
Create a Deployment Script
Now that your machine is connected to CloudRay, let’s create a reusable Bash script to automate the deployment process. You need to follow these steps to create the script in CloudRay.
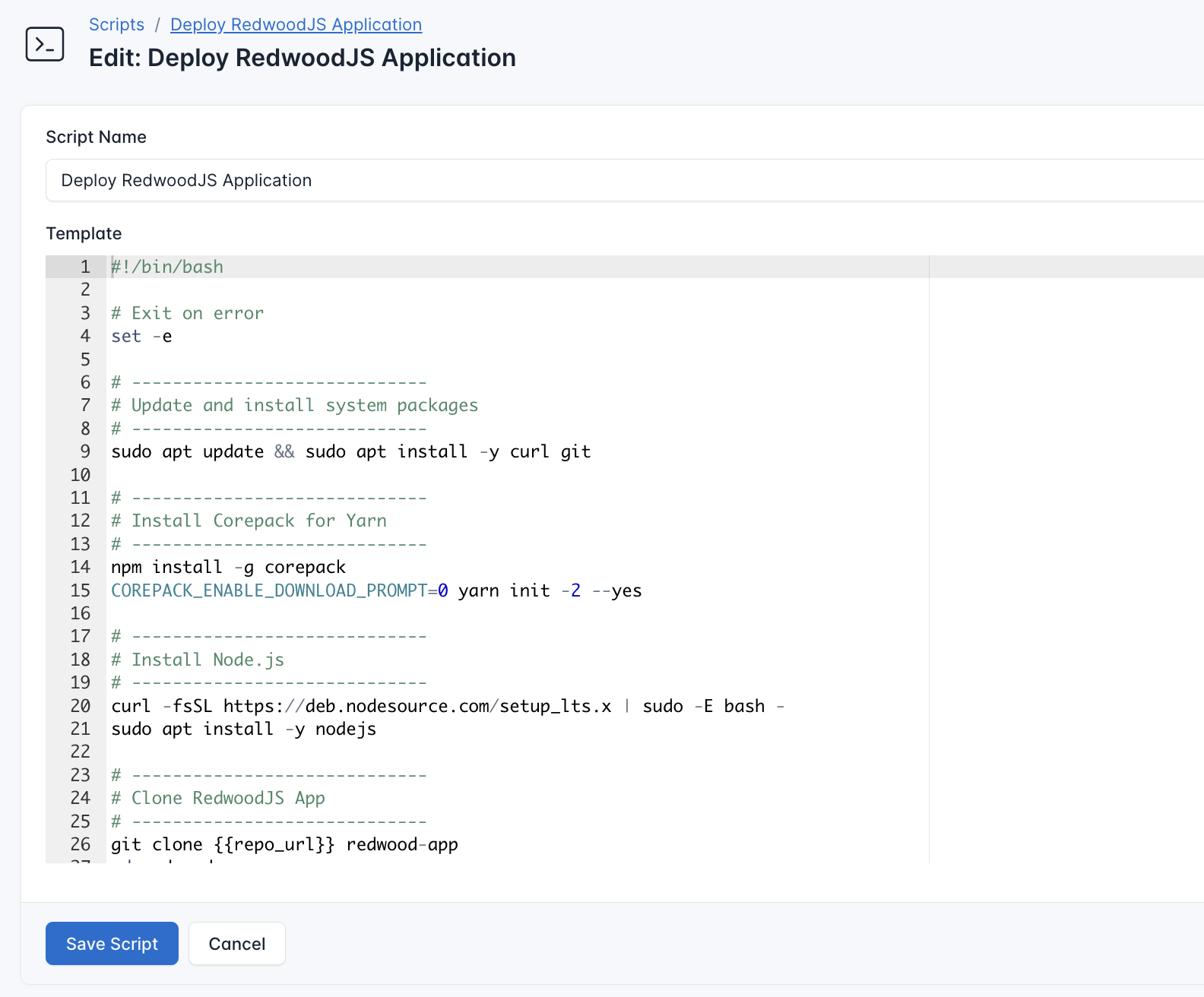
- Go to Scripts in your CloudRay project
- Click New Script
- Name:
Deploy RedwoodJS Application. You can give it any name of your choice - Copy this code:
#!/bin/bash
# Exit on error
set -e
# -----------------------------
# Update and install system packages
# -----------------------------
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y curl git
# -----------------------------
# Install Corepack for Yarn
# -----------------------------
npm install -g corepack
COREPACK_ENABLE_DOWNLOAD_PROMPT=0 yarn init -2 --yes
# -----------------------------
# Install Node.js
# -----------------------------
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt install -y nodejs
# -----------------------------
# Clone RedwoodJS App
# -----------------------------
git clone {{repo_url}} redwood-app
cd redwood-app
# -----------------------------
# Install dependencies and build
# -----------------------------
yarn install
yarn rw g page home /
yarn rw build web
# Install PM2 globally
npm install -g pm2
# Start the RedwoodJS frontend (served from web/dist) on port 3000
pm2 start "serve -s web/dist -l 3000" --name redwood-frontend
# Save the PM2 process list to be resurrected on reboot
pm2 save
# Generate and configure system startup script
pm2 startupHere is what the Deploy RedwoodJS Application script does:
- Installs required dependencies (Node.js, Git, Yarn)
- Clone your Astro project from a Git repository
- Installs dependencies and builds the app
- Serves the frontend from the
web/distdirectory
Define the Variable Group
Now, before running the deployment script, you need to define value for the placeholder {{repo_url}} used in the scrips. CloudRay processes all scripts as Liquid templates. This allows you to use variables dynamically across different servers.
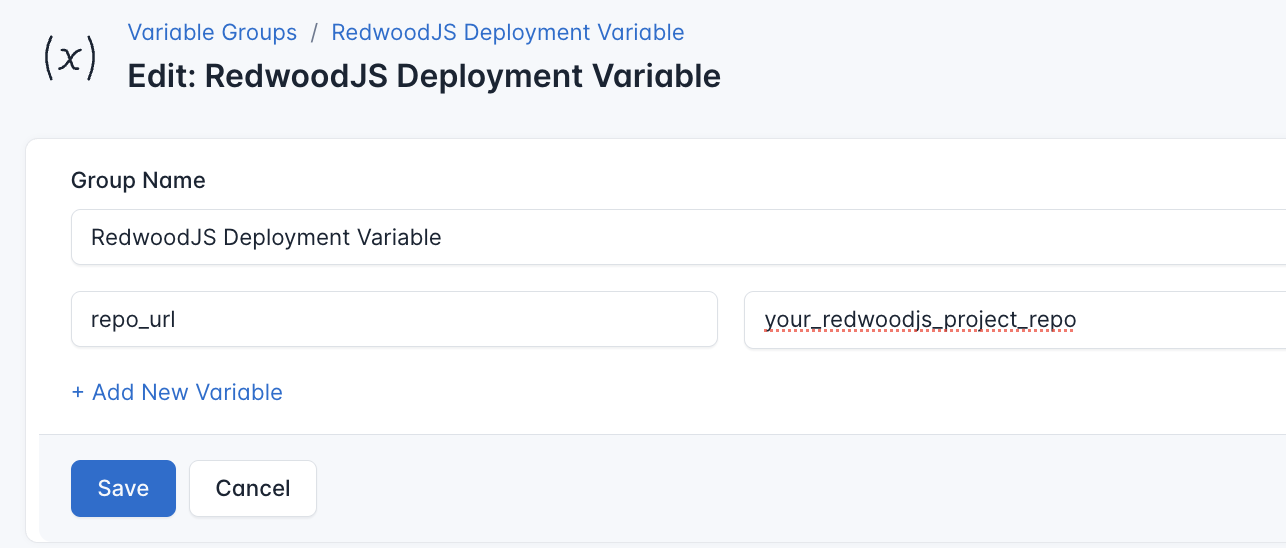
To ensure that these values are automatically substituted when the script runs, follow these steps to create a variable group:
- Navigate to Variable Groups: In your CloudRay project, go to “Scripts” in the top menu and click on “Variable Groups”.
- Create a new Variable Group: Click on “Variable Group”.
- Add the following variables:
repo_url: The URL of your GitHub repository
Since the variables is setup, proceed with running the scripts with CloudRay
Run the Deployment Script
CloudRay uses Runlogs to execute scripts on your servers while providing real-time logs of the execution process.
Once the script is saved, you can deploy your Astro site by creating a Runlog:
- Navigate to Runlogs: In your CloudRay project, go to the Runlogs section in the top menu.
- Create a New Runlog: Click on New Runlog.
- Configure the Runlog: Fill in the required details:
- Server: Select the server you added earlier.
- Script: Choose the “Deploy RedwoodJS Application”
- Variable Group (optional): Select the variable group you created earlier.
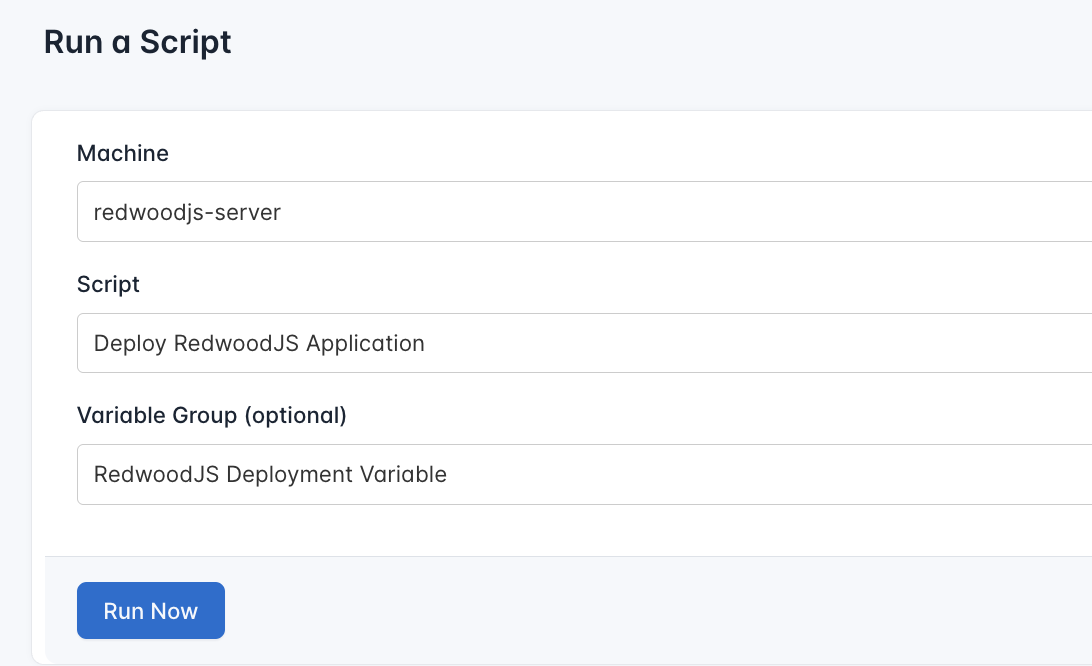
- Execute the Script: Click on Run Now to start the execution.
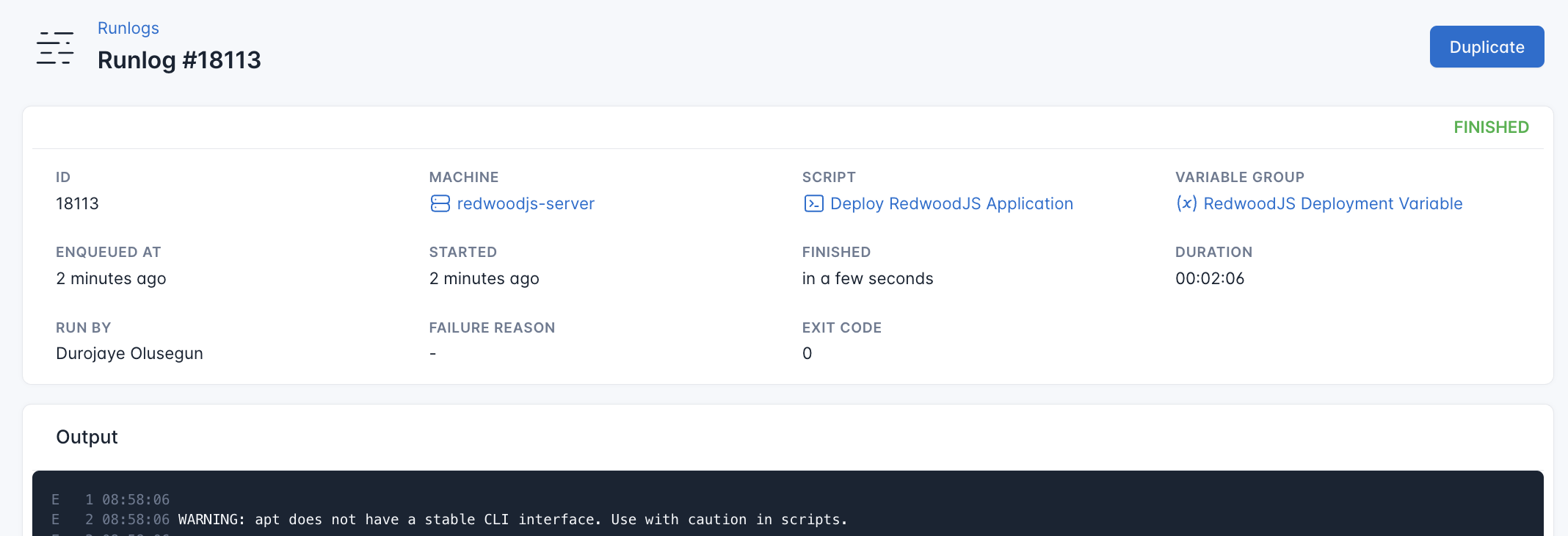
CloudRay will automatically connect to your server, run the Deploy RedwoodJS Application, and provide live logs to track the process. If any errors occur, you can review the logs to troubleshoot the issue.
Once the deployment is complete, you can visit http://<your-server-ip>:3000. You should see your RedwoodJS site up and running.
Next Step
To productionise your deployment:
- You can configure a Nginx reverse proxy to serve on port 80
- Set up HTTPS with Let’s Encrypt
Summary
Deploying a RedwoodJS app with CloudRay streamlines server setup and project provisioning using Bash scripts and dynamic variables. You gain the ability to manage infrastructure and scale your app across environments more easily.
For more deployment guides and use cases, check out our CloudRay Guides or explore the CloudRay Docs.
