Deploy your Express.js application seamlessly with CloudRay. This guide walks you through setting up and automating the deployment process, ensuring your app is always up-to-date.
Contents
- Adding Servers to CloudRay
- Assumptions
- Create the setup script
- Create the Deployment Script
- Create a Variable Group
- Run the setup script
- Run the deployment script
- Related Guides
Adding Servers to CloudRay
Before getting started, make sure your target servers are connected to CloudRay. If you haven’t done this yet, follow our servers docs to add and manage your server.
NOTE
This guide uses Bash scripts, providing a high degree of customisation. You can adapt the scripts to fit your specific deployment needs and environment.
Assumptions
- This guide assumes that the database is hosted on a separate server. Installing and configuring the database on the same server as the Rails application is not within the scope of this document. You can refer to other articles for instructions on setting up a database server.
- This guide assumes you’re using Ubuntu 24.04 LTS as your server’s operating system. If you’re using a different version or a different distribution, adjust the commands accordingly.
Once your server is added, proceed to the next step.
Create the setup script
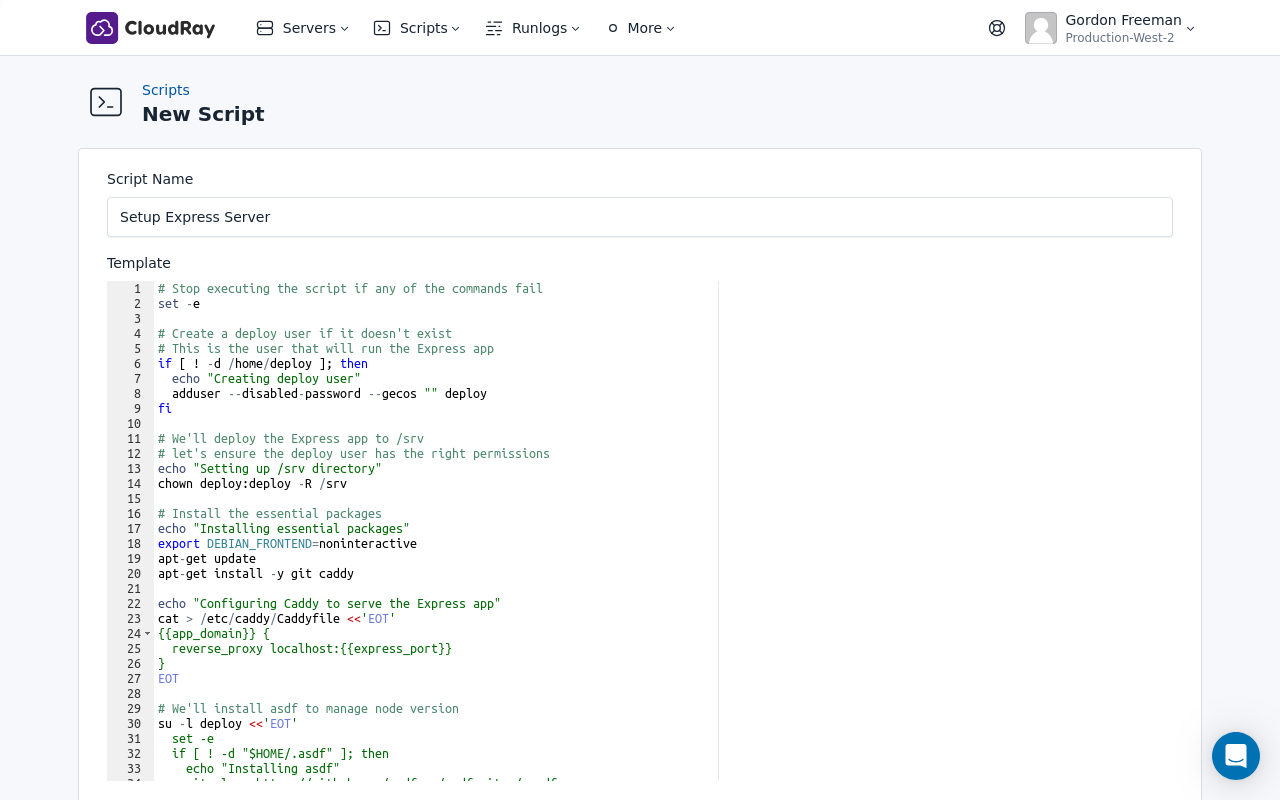
To streamline the deployment process, you’ll need two Bash scripts:
- Setup Script: You’ll run this once when setting up a new server to install dependencies and configure services.
- Deployment Script: You can run this anytime you want to update your application with new code.
In this section, we’ll create the Setup Script.
The setup script prepares your server by:
- Creating a deploy user that runs the Node server using pm2 as a non-privileged service
- Installing Caddy web server for automatic HTTPS
- Setting up asdf to install Node.js
- Creating a systemd service to start pm2 at boot
- Setting up the repository for the first time
To create the setup script:
- Go to Scripts in your CloudRay project
- Click New Script
- Name:
Setup Express Server - Copy this code:
# Stop executing the script if any of the commands fail
set -e
# Create a deploy user if it doesn't exist
# This is the user that will run the Express app
if [ ! -d /home/deploy ]; then
echo "Creating deploy user"
adduser --disabled-password --gecos "" deploy
fi
# We'll deploy the Express app to /srv
# Let's ensure the deploy user has the right permissions
echo "Setting up /srv directory"
chown deploy:deploy -R /srv
# Install the essential packages
echo "Installing essential packages"
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
apt-get update
apt-get install -y git caddy
echo "Configuring Caddy to serve the Express app"
cat > /etc/caddy/Caddyfile <<'EOT'
{{app_domain}} {
reverse_proxy localhost:{{express_port}}
}
EOT
# We'll install asdf to manage node version
su -l deploy <<'EOT'
set -e
if [ ! -d "$HOME/.asdf" ]; then
echo "Installing asdf"
git clone https://github.com/asdf-vm/asdf.git ~/.asdf
echo "source $HOME/.asdf/asdf.sh" >> ~/.bashrc
else
echo "Updating asdf"
cd ~/.asdf
git pull
fi
source $HOME/.asdf/asdf.sh
if ! grep -q "legacy_version_file" ~/.asdfrc; then
echo "legacy_version_file = yes" >> ~/.asdfrc
fi
asdf plugin add nodejs
echo "Installing Node.js version {{node_version}}"
asdf install nodejs {{node_version}}
asdf reshim
asdf global nodejs {{node_version}}
npm install -g pm2
echo "Finished installing Node.js"
EOT
echo "Creating the pm2 startup service"
export ASDF_DIR=/home/deploy/.asdf
export ASDF_DATA_DIR=/home/deploy/.asdf
source /home/deploy/.asdf/asdf.sh
asdf shell nodejs {{node_version}}
pm2 startup systemd -u deploy --hp /home/deploy
echo "Setting up the repository for the first time"
su -l deploy <<'EOT'
set -e
source "$HOME/.asdf/asdf.sh"
mkdir -p /srv/{{app_name}}
cd /srv/{{app_name}}
if [ ! -d "/srv/{{app_name}}/.git" ]; then
git clone https://{{github_access_token}}@github.com/{{github_repo_name}} .
fi
npm install
pm2 stop {{app_name}} || true
env PATH="$(asdf where nodejs)/bin:$PATH" pm2 start npm --name {{app_name}} -- start
pm2 save
EOT
systemctl restart caddy.service
echo "Done."TIP
If you find this script too long to manage, you can break it into smaller scripts and use Script Playlists to run them together.
Create the Deployment Script
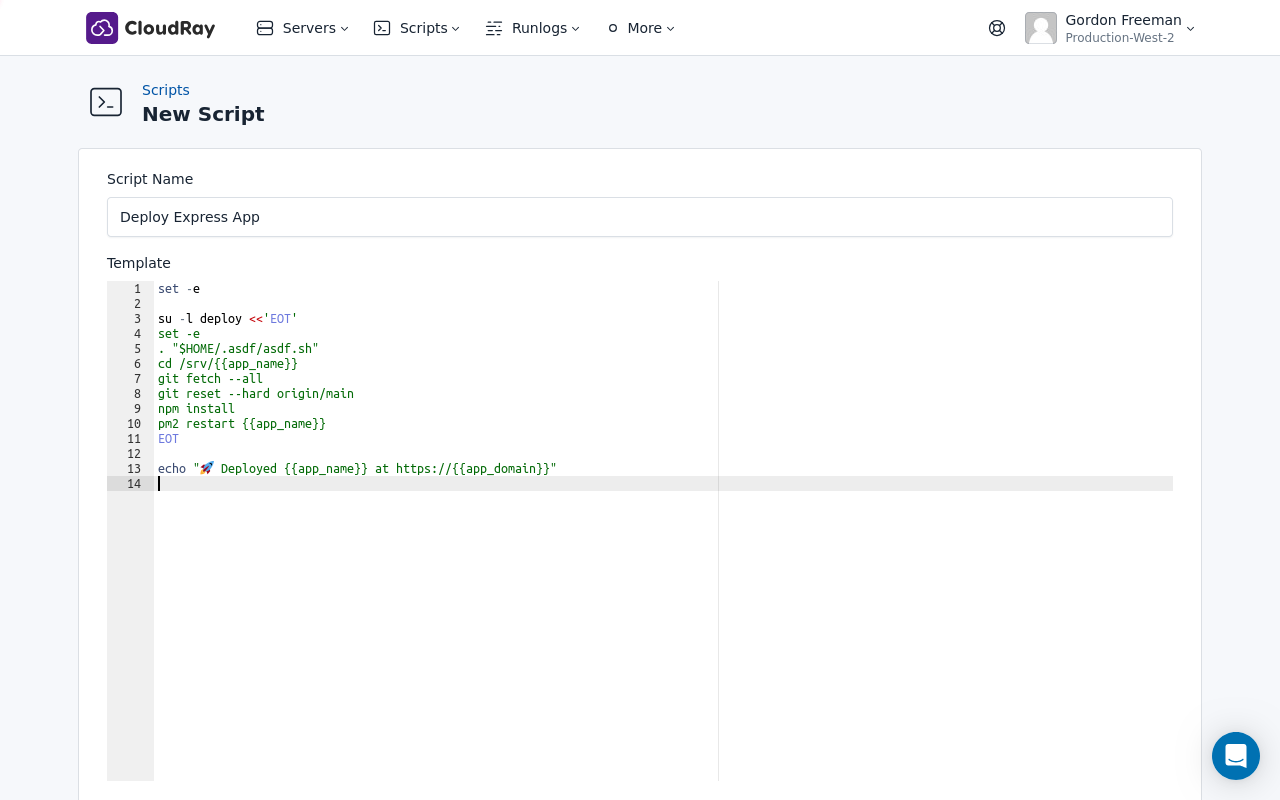
You’ll use this script whenever you want to update your application. The script:
- Pulls latest code from your Git repository’s main branch
- Installs app dependencies
- Restarts the Node server using pm2
To create the deployment script:
- Go to Scripts > New Script
- Name:
Deploy Express App - Add code:
set -e
su -l deploy <<'EOT'
set -e
. "$HOME/.asdf/asdf.sh"
cd /srv/{{app_name}}
git fetch --all
git reset --hard origin/main
npm install
pm2 restart {{app_name}}
EOT
echo "🚀 Deployed {{app_name}} at https://{{app_domain}}"Create a Variable Group
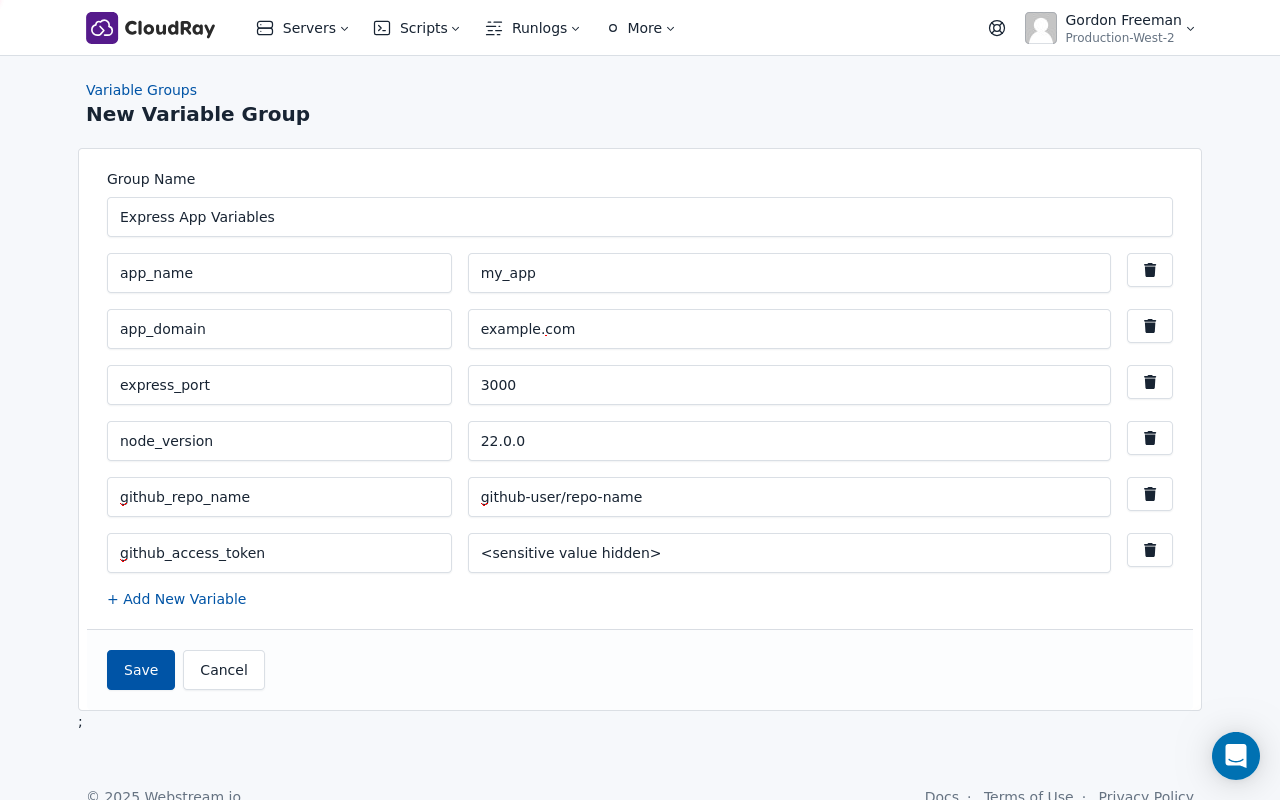
Our scripts use variables like {{app_name}}, {{app_domain}}, and {{node_version}} because CloudRay processes all scripts as Liquid templates. This allows you to use placeholders in your scripts, making them dynamic and reusable across different servers.
To provide values for these variables, you’ll need to create a variable group. Here’s how:
- Navigate to Variable Groups: In your CloudRay project, go to “Scripts” in the top menu and click on “Variable Groups”.
- Create a new Variable Group: Click on “New Variable Group”.
- Add the following variables:
app_name: Your application’s name (use underscores instead of spaces), e.g.,my_appapp_domain: Your application’s domain name, e.g.,myapp.example.comnode_version: The version of Node.js you want to install. E.g.,20.0.0express_port: The port your Express application listens on (e.g.,3000)github_access_token: Your GitHub personal access token for cloning the repository.github_repo_name: Your GitHub repository in the formatusername/repository, e.g.,yourusername/your-repo.
Run the setup script
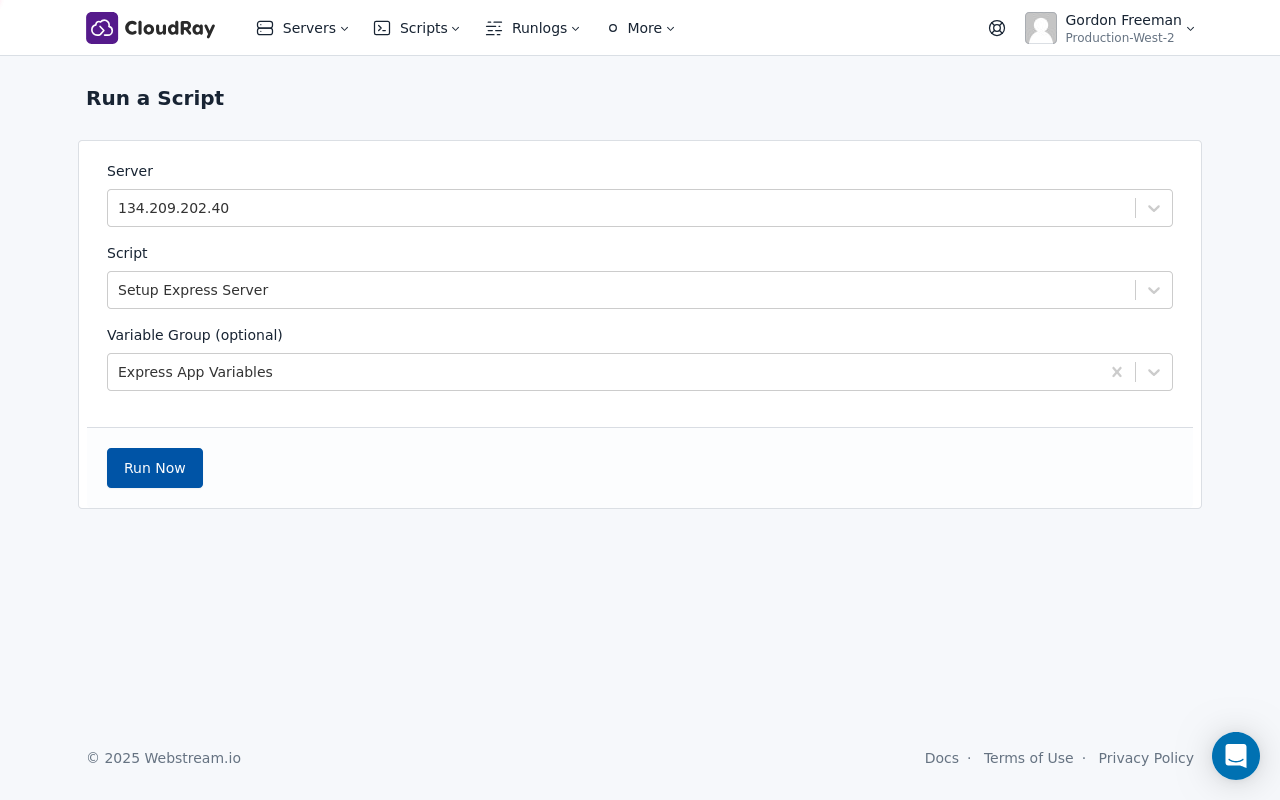
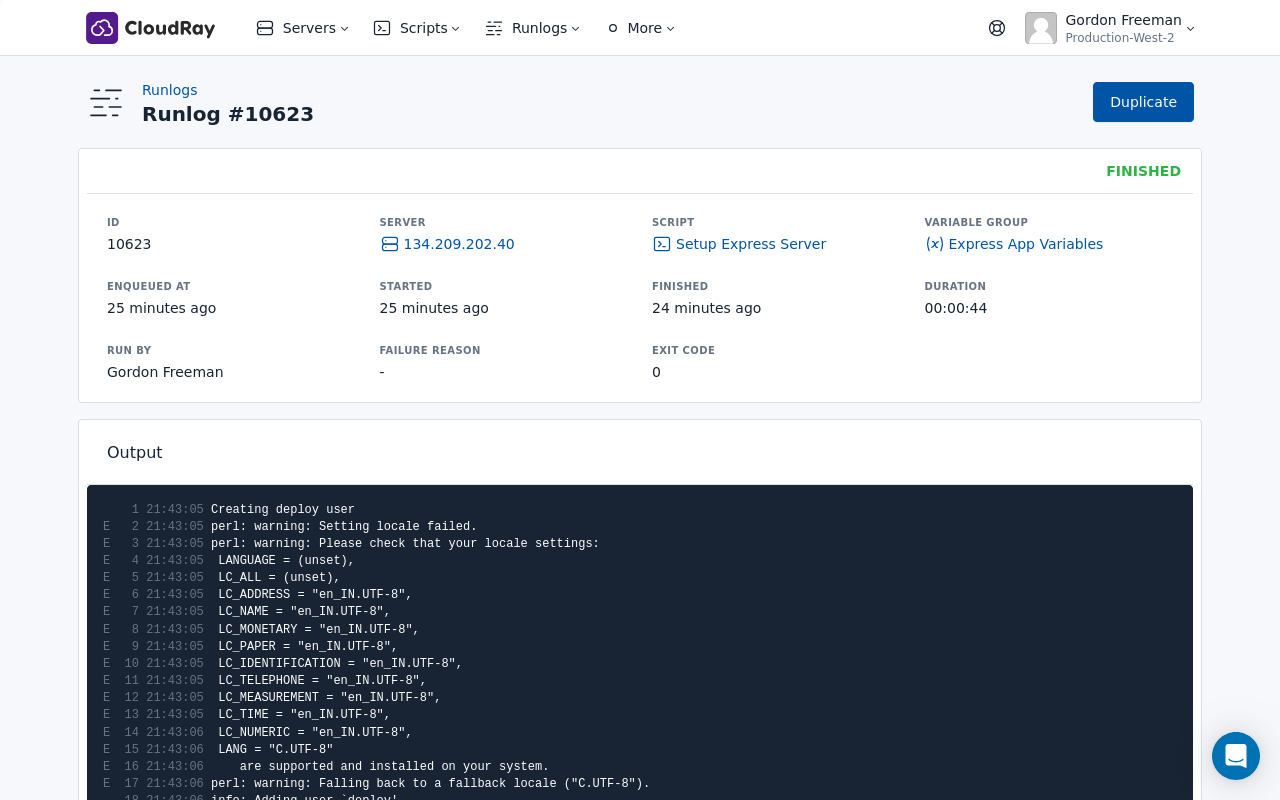
To run the Setup Express Server script, you’ll use a Runlog in CloudRay. A Runlog allows you to execute scripts on your servers and provides detailed logs of the execution process.
Here’s how to create and run a Runlog:
- Navigate to Runlogs: In your CloudRay project, go to “Runlogs” in the top menu.
- Create a new Runlog: Click on “New Runlog”.
- Fill in the form:
- Server: Select the server you added earlier.
- Script: Choose the
Setup Express Serverscript. - Variable Group: Select the variable group you created earlier.
- Run the script: Click on “Run” to execute the script on your server.
CloudRay will connect to your server, run the Setup Express Server script, and show you the live output as the script executes.
Run the deployment script
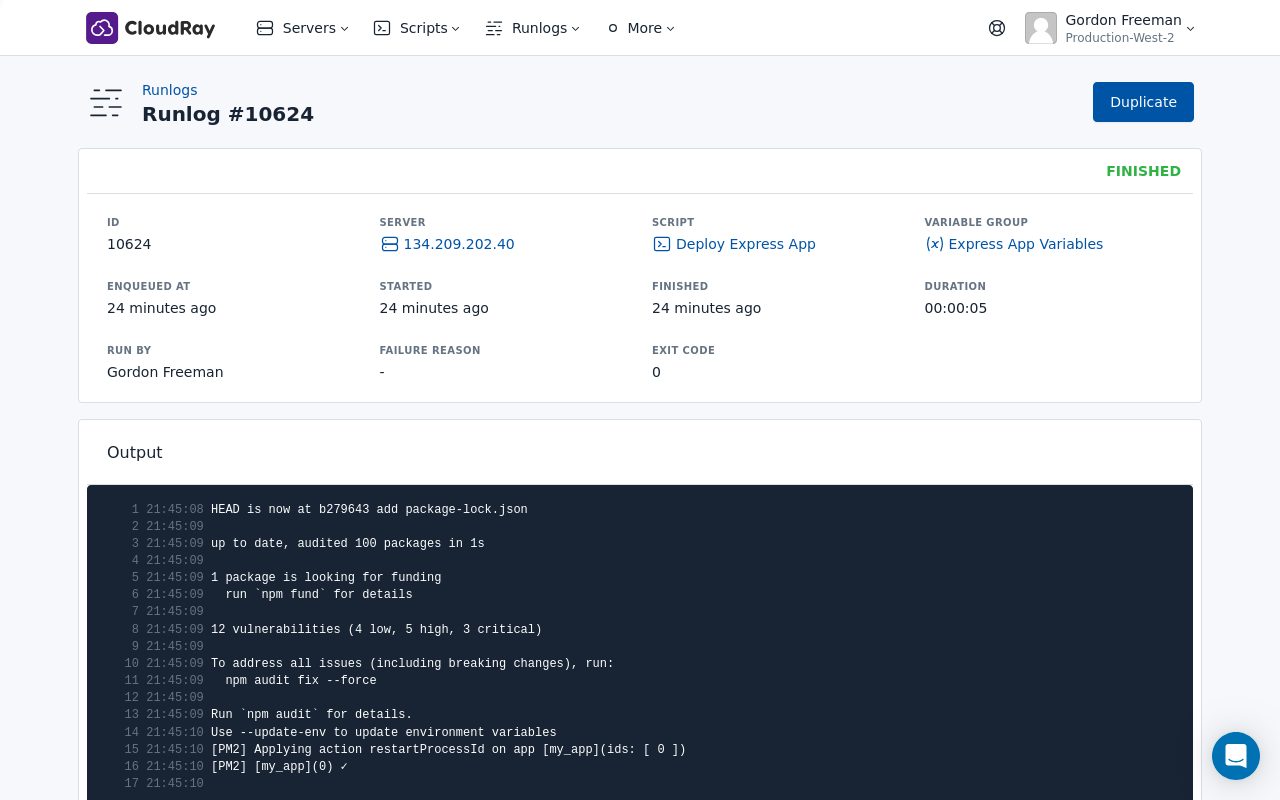
You can run the deploy-rails-app script whenever you want to deploy a new version of your application. Here’s how to create a Runlog for the deployment script:
- Navigate to Runlogs: In your CloudRay project, go to “Runlogs” in the top menu.
- Create a new Runlog: Click on “New Runlog”.
- Fill in the form:
- Server: Select the server you added earlier.
- Script: Choose the
Deploy Express Appscript. - Variable Group: Select the variable group you created earlier.
- Run the script: Click on “Run” to execute the script on your server.
CloudRay will connect to your server, run the Deploy Express App script, and show you the live output as the script executes.
That’s it! Happy deploying!
Related Guides
- Deploy Ruby on Rails
- Deploy Jenkins with Docker Compose
- Deploy Laravel
- Deploy SonarQube
- Deploy Static Website from GitHub
- Deploy Next.js Application
Olusegun Durojaye
CloudRay Engineering Team
